Debugging RAG Chatbots and AI Agents with Sessions
When does your AI agent start hallucinating in the multi-step process? Have you noticed consistent issues with a specific part of your agentic workflow?

These are common questions we faced when building our own RAG-powered chatbots and AI agents. Getting reliable responses and minimizing errors like hallucination was incredibly challenging, without visibility into how our users interacted with our large language models.
In this guide, we explore common AI agent pitfalls, how to debug multi-step processes using Helicone's Sessions, and the best tools for building reliable, production-ready AI agents.
What you will learn:
- AI agents vs. traditional chatbots
- Components of an AI agent
- Challenges of debugging AI agents
- How to debug AI agents using Sessions
- 6 Popular agent debugging tools
AI Agents vs. Traditional Chatbots
Unlike traditional chatbots, which follow explicit instructions or rules, AI agents can autonomously perform specific tasks with advanced decision-making abilities. They interact with their environment by collecting data, processing it, and deciding on the best actions to achieve a predefined goal.
Examples of AI Agents
| What it does | Example | |
|---|---|---|
| Copilots | Help users by providing suggestions and recommendations | Suggest code snippets, highlight potential bugs, and offer optimization tips. Developer decides whether to implement suggestions. |
| Autonomous Agents | Perform tasks independently without human intervention | Handle customer inquiries by identifying issues, accessing account info, processing refunds, updating account details, and responding to customers. Can escalate to human agents when needed. |
| Multi-Agent Systems | Involve interactions and collaboration between multiple autonomous agents to achieve collective goals | Leverage advantages like dynamic reasoning, distributed task handling, and improved memory retention for information. |
Use of RAG to Improve Functionality
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an advanced method that allows the agent to incorporate information from external knowledge bases (e.g., databases, documents, articles) into the response.
RAG significantly improved the response outcome as the agent now have access to the most recent data based on keywords, semantic similarity, or other advanced search techniques, and used it to generate more accurate, personalized, and context-specific responses.
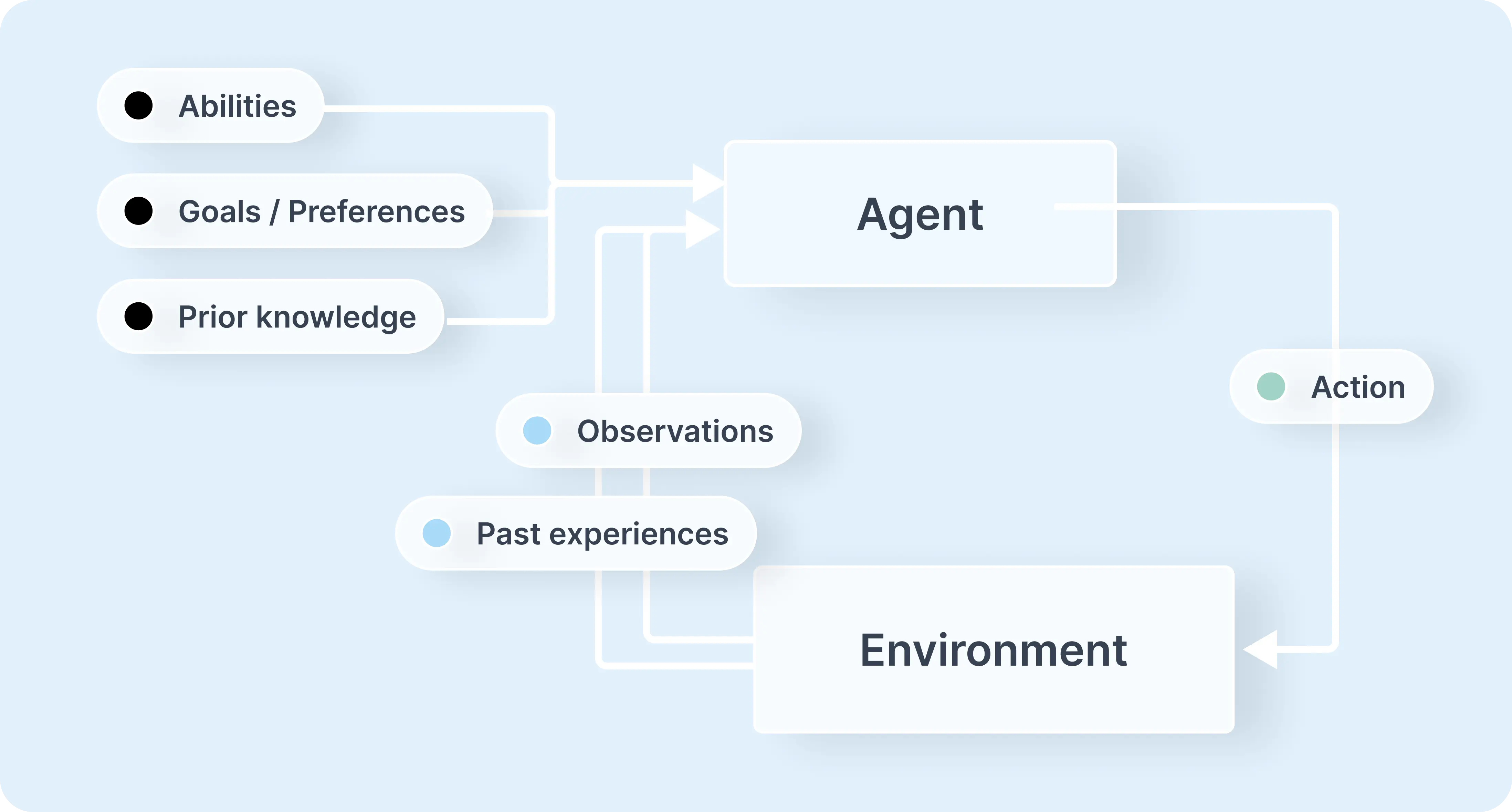
Core Components of AI Agents
Typically, AI agents consists of four core components:
-
Planning: When you define a goal, agents will plan, sequence actions and formulate strategies.
-
Tool / Vector DB Calls: Advanced AI Agents can interact with external tools, APIs, and services through function calls in order to handle more complicated tasks.
For example:
- Fetching real-time weather data or stock prices.
- Using translation services.
- Performing image recognition or editing using specialized libraries.
- Running custom scripts to automate workflow.
-
Perception: AI agents can also process information from their environment, making them more interactive and context-aware.
This sensory information can include visual, auditory, or other types of data, to help the agents respond appropriately to environmental cues.
-
Memory: AI agents are able to remember past interactions, including tools previously used and its planning decisions. These context are stored to help agents self-reflect and inform future actions.
Challenges of Debugging AI Agents
⚠️ Their decision making process is complicated.
AI agent's adaptive behavior makes their decision paths non-deterministic and harder to trace. This is because agents base their decisions on many inputs from diverse data sources (i.e. user interactions, environmental data, and internal states), and they learn through patterns and correlations identified in the data.
⚠️ No visibility into their internal states.
AI agents function as "black boxes” and understanding how they transform inputs into outputs is not straightforward. Often times, whenever the agent interacts with external services, APIs or other agents, their behavior is unpredictable.
⚠️ Context builds up over time, so do errors.
Agents can often make multiple dependent vector database calls within a single session, adding some complexity in tracing the data flow. They can also operate over a longer sessions, where an early error can have cascading effects, so it's difficult to identify their original source without proper session tracking.
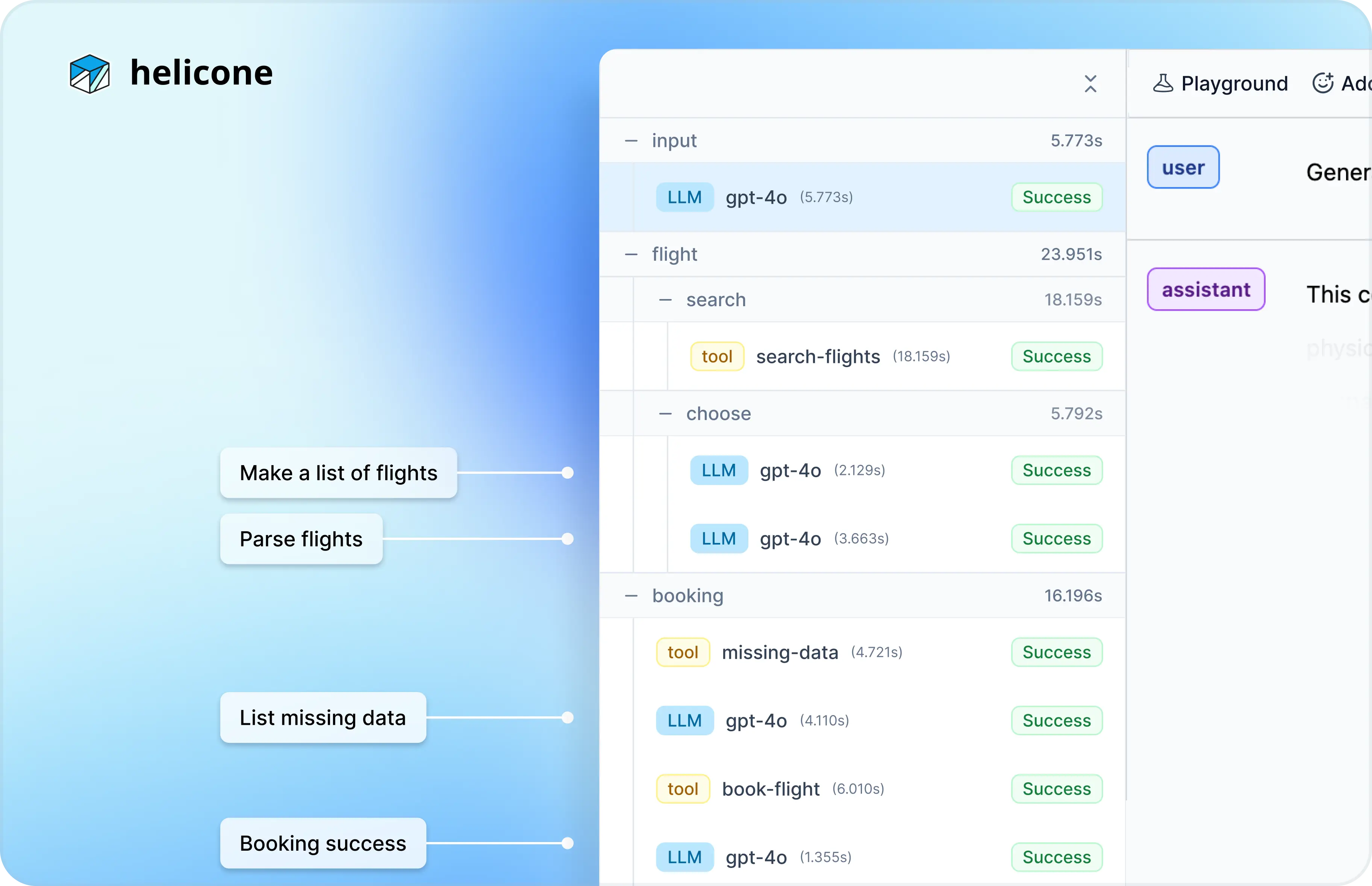
Scenario 1: Debugging errors in a travel chatbot
A travel chatbot assists users in booking flights, hotels and rent cars. There are often issues with data parsing or third-party integrations. Users are frustrated with incomplete bookings.
Issue
While building this chatbot, we noticed that the LLM occasionally provided incorrect parameters to the flight search API, leading to incorrect bookings.
How to debug using Helicone's Sessions
-
Go to the
Sessionstab, find related requestsTo examine what's causing the error, go to
Sessions. Check out the requests that relates to the action where the error occured.In this case it's the
search-flightsAPI call. -
Take a closer look at the request
Next, click on the request to inspect its details.
For example, the user input says:
I've just arrived at JFK, where can I go to reLAX?In this case, the LLM misinterpreted capitalized words as airline abbreviations, mistakenly assuming the user wants to book a flight from
JFK(New York) toLAX(Los Angeles). -
Fix the bug in Playground
To fix this, we go to
Playgroundand improve the prompt to ignore capitalized words.We discovered that by converting the entire string to lowercase before passing it to the LLM, the LLM was able to correctly parse airport codes while ignoring unrelated capitalized words.
Unfortunately, there are no flights available from JFK at the moment that match your search for relaxation destinations. You might want to consider checking for flights at different times or days, or you could explore relaxing spots within the airport such as lounges or nearby hotels.
The chatbot now accurately interprets user intent and returns the correct departure and arrival airports, leading to more reliable flight search results.
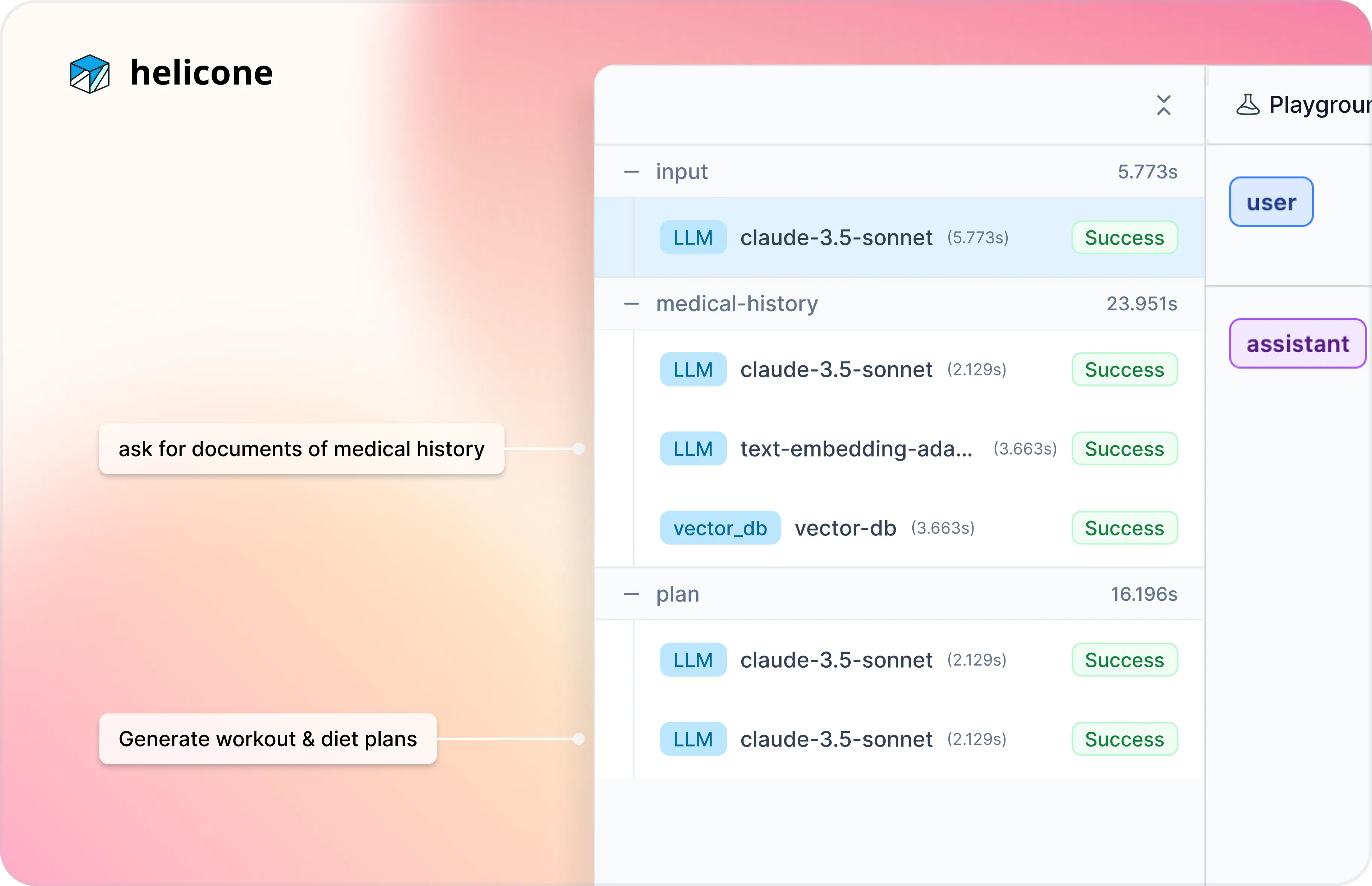
Scenario 2: Personalize responses to match user intent
A health and fitness chatbot that takes the user's goal to create a personalized workout and dietary plans.
Issue
Users report that the chatbot is generating inconsistent dietary recommendations when prompted a few times.
In this example, the user who previously selected a high-protein diet for muscle gain might later receive a low-calorie meal plan designed for weight loss.
How to debug using Helicone's Sessions
-
Go to the
SessionstabIdentify recent session logs for users who reported unexpected diet plan changes.
As a first step, verify that users' medical records are being correctly analyzed.
-
Analyze the "Medical History" retrieval step
In the
medical-historytrace, check if the chatbot is correctly retrieving users' medical history data from the vector database.In this case, we found that the LLM failed to lookup relevant user data from the vector DB, causing inconsistencies in retrieved dietary preferences.
-
Fix bug in code
Upon reviewing the code, a bug was found in the data embedding process, leading to incorrect storage and retrieval of user data.
After fixing the issue, tests in the
Playgroundconfirmed that the chatbot now consistently provides diet plans that align with user goals.
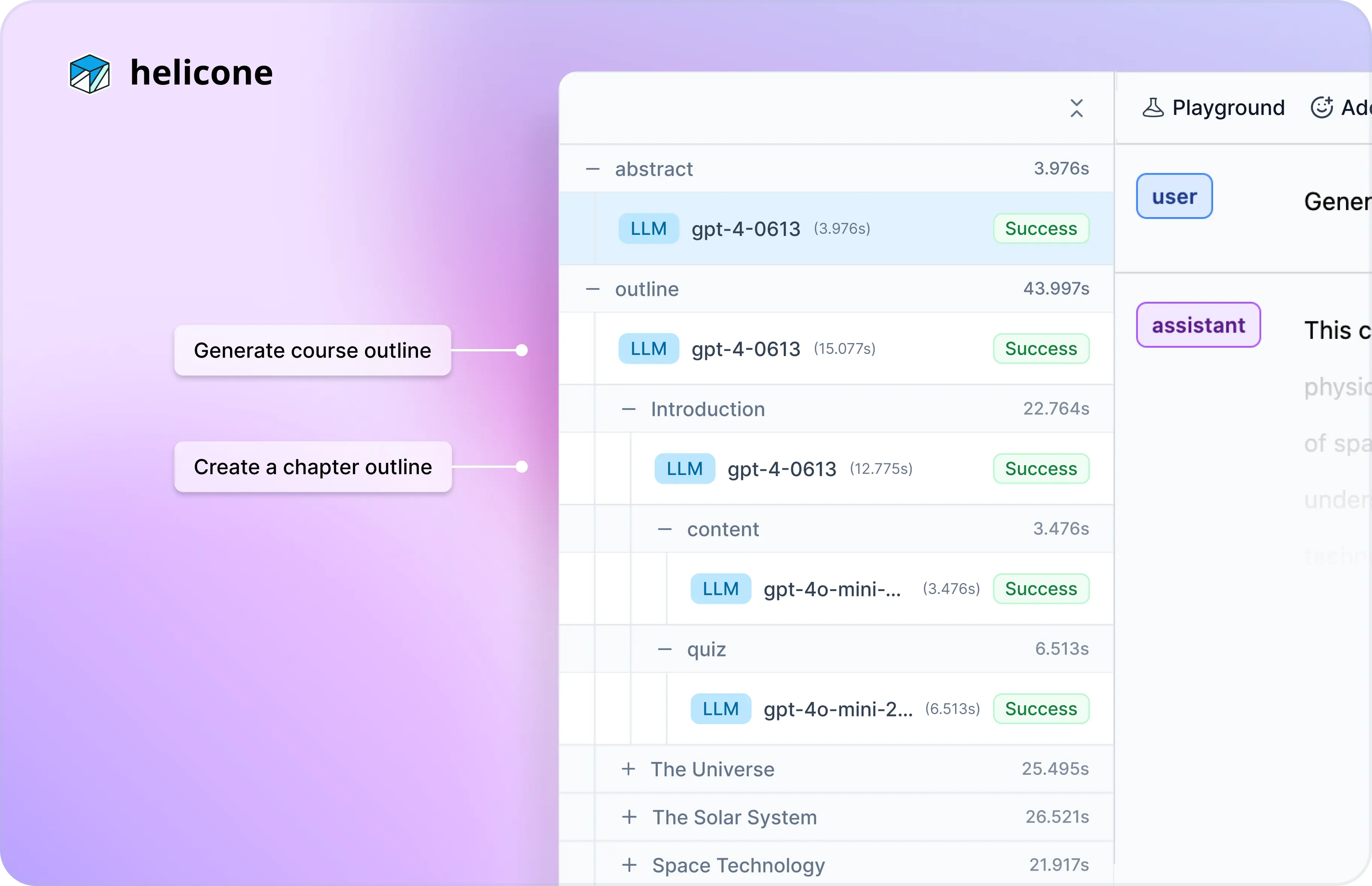
Scenario 3: Create custom learning materials
An AI tutoring service built an AI agent that creates customized learning materials. It's important that the agent generates both accurate and comprehensive lessons.
How to debug using Helicone's Sessions
The Session view will outline the structure of the generated course. Each trace in a Session shows you how the agent interpreted your requests and the corresponding content.
Skimming through, wherever the agent misunderstood topics or failed to cover key concepts, you can then fine-tune that specific prompt using the Playground or Experiments. The goal here is to generate a more thorough content while making sure it is appropriate for the student’s learning level.
6 Popular Agent Debugging Tools
One way we try to debug agents is by understanding the internal workings of the model. We also realized that traditional logging methods often lack the granular data to effectively debug complex behaviors.
However, there are tools to help streamline the debugging process:
1. Helicone open-source
Helicone's Sessions is ideal for teams looking to intuitively visualize agentic workflows. It's catered to both developers building simple and advanced agents that need to group related LLM calls, trace nested agent workflows, quickly identify issues, and track requests, response and metadata to the Vector Database.
2. AgentOps
AgentOps can be a good choice for teams looking for a comprehensive solution to debug AI agents. Despite a less intuitive interface, AgentOps offers comprehensive features for monitoring and managing AI agents.
3. Langfuse
Langfuse is ideal for developers who prefer self-hosting solutions and have simpler infrastructure needs. It offers features similar to Helicone's and is well-suited for projects with modest scalability requirements or those prioritizing local deployment over cloud-based solutions.
4. LangSmith
LangSmith is ideal for developers working extensively with the LangChain framework as its SDKs and documentation are designed to support developers within this ecosystem best.
5. Braintrust
Braintrust is a good choice for those focusing on evaluating AI models. It’s an effective solutions for projects where model evaluation is a primary concern and agent tracing is a secondary need.
6. Portkey
Portkey is designed for developers looking for the latest tools to track and debug AI agents. It introduces new features quickly, great for teams needing the newest suite of features and willing to face the occasional reliability and stability issues.
Building Production-Ready AI Agents
We're already seeing AI agents in action across various fields like customer service, travel, health and fitness, as well as education. However, for AI agents to be truly production-ready and widely adopted, we need to continue to improve their reliability and accuracy.
This requires us to actively monitor their decision-making processes and get a deep understanding of how inputs influence outputs. The most effective way is by using monitoring tools that provide you the insights to make sure your AI agents consistently deliver the results you want.
Additional Resources
- How to set up Sessions
- How to log Vector DB calls with Helicone's Javascript SDK
- How to Optimize AI Agents by Replaying LLM Sessions
- 6 open-source frameworks for building AI agents
Questions or feedback?
Are the information out of date? Please raise an issue or contact us, we'd love to hear from you!