How to Implement Effective LLM Caching
Deploying LLMs is challenging. There is the high operational costs with API calls, latency due to processing time, and scalability limitations when handling large volumes of requests.
In this guide, we will take a deep dive into effective caching strategies for building scalable and cost-efficient LLM applications, with practical implementation tips.
- What is LLM Caching?
- Types of LLM Caching Strategies
- Caching Design Patterns
- Use Cases for LLM Caching
- How to Monitor and Improve Cache Performance
Let's get into it!

What is LLM Caching?
LLM caching is the process of storing and reusing previously computed responses from a large language model (LLM). Instead of generating a new response for every request, caching enables quick retrieval of results, reducing both response times and computational costs.
Without caching, every user request requires a full computation, even if the same query has been processed before. Implementing an effective caching strategy mitigates these issues, making LLM applications more responsive and cost-efficient.
Types of LLM Caching Strategies
There are two primary LLM caching strategies: exact key caching and semantic caching.
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| Exact Key Caching | Fast retrieval, simple implementation | Sensitive to minor variations in input, such as added spaces or typos |
| Semantic Caching | Handles reworded queries, increases cache hit rate | Potential false positives (e.g., similar prompts leading to unintended cached responses) |
1. Exact Key Caching
Exact key caching works by storing responses for specific input queries. If a user submits the exact same input, the cached response is returned instead of querying the LLM again.
Example:
# First request (cache miss): 4 seconds
response_1 = openai.Completion.create(
model="gpt-4",
prompt="What is OpenAI?"
)
# Second request (cache hit): 0.03 seconds
response_2 = openai.Completion.create(
model="gpt-4",
prompt="What is OpenAI?"
)
Bottom Line
Exact key caching is a simple and fast retrieval method that works well for applications with few unique queries. However, it is sensitive to minor variations in input, such as added spaces or typos.
2. Semantic Caching
Semantic caching stores responses based on meaning rather than exact input. If two inputs have similar intent, the cached response is used.
Example:
# First request: 5 seconds
response_1 = openai.Completion.create(
model="gpt-4",
prompt="Explain caching in AI."
)
# Similar request (cache hit using semantic match): 1 second
response_2 = openai.Completion.create(
model="gpt-4",
prompt="Can you describe AI caching?"
)
Bottom Line
Semantic caching is a more flexible method that increases cache hit rate and handles queries that are similar well. However, it can lead to potential false positives.
Caching Design Patterns
1. Single LLM Caching Layer
A single caching layer sits between the user and the LLM, checking for cached responses before forwarding requests to the model.
The workflow is as follow:
- User submits a query.
- Cache checks for an exact match.
- If found, returns the cached response.
- If not, forwards the request to the LLM, stores the response, and returns it.
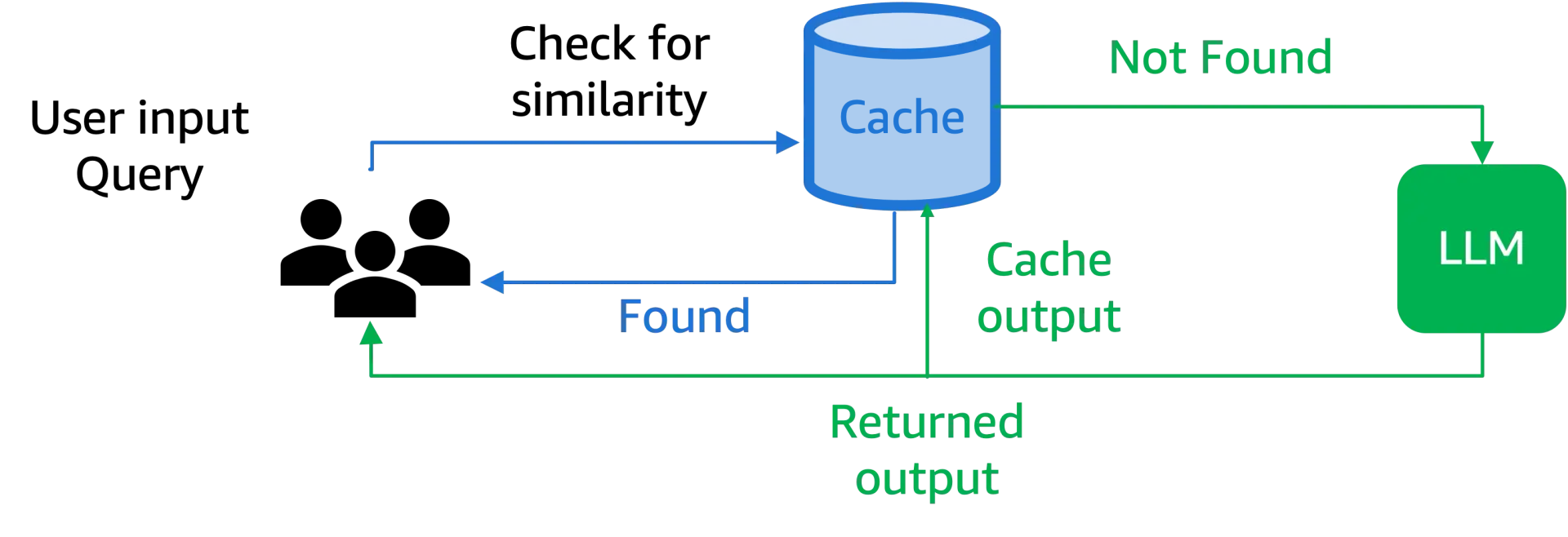
Image source: Bridging the Efficiency Gap: Mastering LLM Caching for Next-Generation AI
2. Multi-Layer Caching
A multi-layer caching system enhances response retrieval by incorporating multiple levels of caching techniques, optimizing both speed and relevance of stored results.
A simple multi-layer system may work like this:
-
Layer 1: Exact Key Matching
- This layer checks for an exact match of the input query in the cache. If a match is found, the cached response is returned immediately, ensuring the fastest possible retrieval.
- Example: If a user asks "What is Photosynthesis?" and the same query exists in the cache, the precomputed response is delivered instantly.
-
Layer 2: Semantic Caching
- If no exact match is found, the request is processed through a semantic caching layer, which uses NLP techniques to detect similar queries and retrieve an appropriate response.
- Example: If the query "Explain Photosynthesis" is submitted, semantic caching may recognize it as similar to "What is Photosynthesis?" and return the corresponding cached response, even if it is not an exact match.
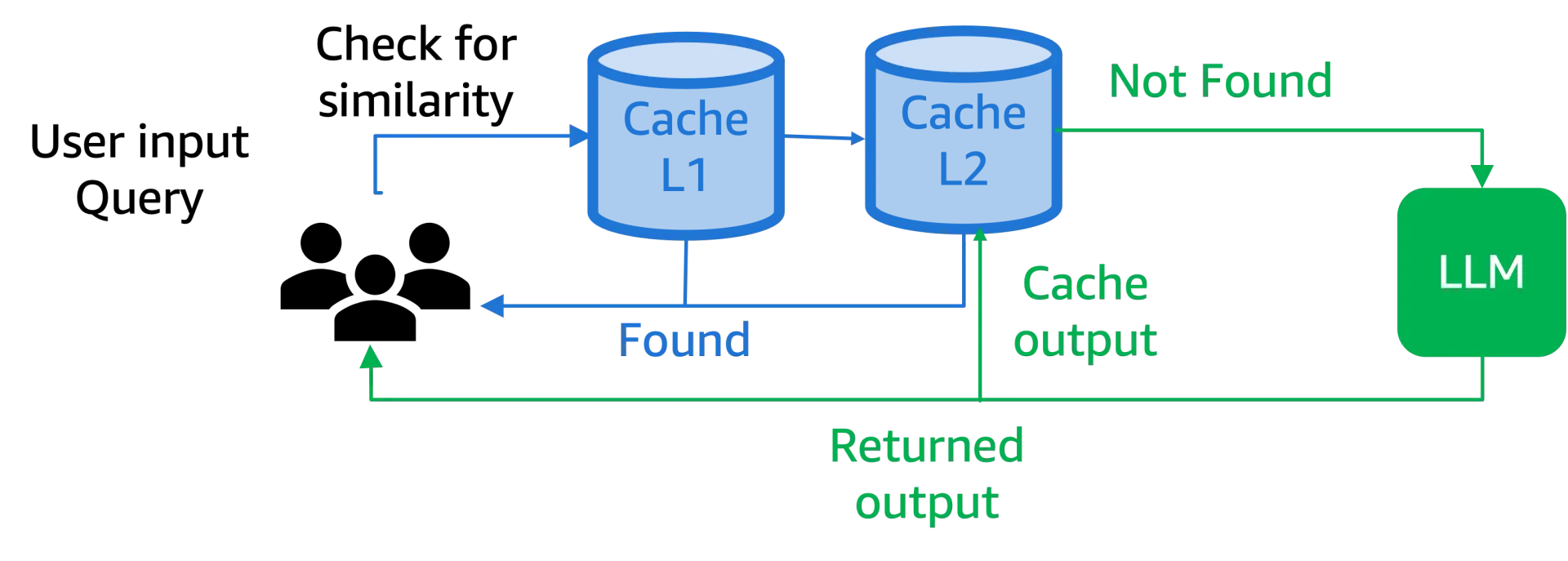
Image source: Bridging the Efficiency Gap: Mastering LLM Caching for Next-Generation AI
By using this hierarchical structure, multi-layer caching ensures a higher cache hit rate, reduces redundant model invocations, and maintains a balance between precision and flexibility.
This approach is particularly useful for applications with diverse user queries, improving overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
3. RAG-Based Caching
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) models use caching in two ways:
- Pre-Retrieval Caching: Stores retrieved documents before LLM processing, reducing repeated knowledge base lookups.
- Post-Retrieval Caching: Stores responses after document retrieval, avoiding unnecessary model invocations. This method ensures users receive fast responses while still using up-to-date data.
Pros: Reduces latency for knowledge-intensive applications
Cons: Requires careful management to prevent outdated responses
Use Cases for LLM Caching
| Use Case | Example |
|---|---|
| Customer Support Bots | Reduce response time for frequent queries (e.g., "How do I reset my password?") |
| Search Engines | Store frequently searched terms to reduce API calls and improve latency |
| Recommendation Systems | Cache personalized content recommendations for repeat users |
| Content Generation | Save AI-generated responses for similar creative writing or art prompts to speed up the generation of new ones |
How to Monitor and Improve Cache Performance
1. Optimizing cache hit rates
You can maximize cache hit rates by:
- Increasing cache duration for high-frequency queries
- Using both exact and semantic caching
Make sure to monitor and analyze access patterns to improve your caching rules over time.
2. Balancing cache size with memory usage
A larger cache can store more data but it also consumes more memory.
The good thing is, you can update your cache expiration policies and eviction strategies such as Least Recently Used (LRU) to maintain efficiency.
You can also use monitoring tools to track memory impact more easily and make adjustments.
Which leads us to...
3. Using monitoring tools
A common theme when it comes to optimizing cache performance is extensive monitoring—this is where tools like Helicone come in.
Helicone provides powerful observability features to monitor and optimize LLM caching performance. You gain access to real-time insights that help fine-tune your caching strategy for maximum efficiency.
![]()
What developers use Helicone for:
- Track cache hits/cache misses.
- Analyze cost and latency with each requests
- Remove unnecessary LLM calls and lower operational expenses.
- Customize cache settings such as cache duration, bucket sizes and use cache seeding to maintain predictable responses.
- Access a real-time dashboard for detailed analytics.
How to Enable Caching with Helicone
Enabling caching with Helicone requires just one line of code. Cache your LLM requests with Helicone in a minute:
openai.api_base = "https://oai.helicone.ai/v1"
response = openai.Completion.create(
model="gpt-4",
prompt="Define machine learning",
extra_headers={
"Helicone-Cache-Enabled": "true", # simply add this header and set to true
"Cache-Control": "max-age=86400"
}
)
Bottom Line
LLM caching is essential for reducing costs, improving response times, and scaling AI applications efficiently.
Using a mix of exact and semantic caching, along with appropriate architectural patterns—made simple with tools like Helicone—you can Implement caching today to make your LLM applications faster and more cost-effective.
You might also like:
- 5 Powerful Techniques to Slash Your LLM Costs
- 4 Essential Helicone Features to Optimize Your LLM App Performance
- Helicone vs. Arize Phoenix: Which is the Best LLM Observability Platform?
Questions or feedback?
Are the information out of date? Please raise an issue or contact us, we'd love to hear from you!